Can Divorce Petition Be Amended? Complete Guide to Amendment Rules
Yes, a divorce petition can be amended in India under specific circumstances and legal procedures. The amendment process allows parties to modify their original petition to include new grounds, correct errors, or update information that has changed since filing.
Understanding when and how to amend a divorce petition is crucial for ensuring your case proceeds smoothly. The legal framework provides clear guidelines for making necessary changes to strengthen your position.
Legal Framework for Petition Amendment
The Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, under Order 6 Rule 17, governs the amendment of pleadings in civil courts. This rule applies to divorce petitions filed in family courts across India.
Courts have discretionary power to allow amendments at any stage of proceedings. The primary consideration is whether the amendment serves the interests of justice without causing undue prejudice to the opposing party.
When Can You Amend a Divorce Petition?
Before Service of Summons
Amendments are most easily granted before the petition is served to the respondent. At this stage, courts typically allow amendments without requiring detailed justification.
You can correct factual errors, add new grounds for divorce, or modify claims regarding custody and maintenance. The process remains straightforward with minimal court intervention required.
After Service But Before Evidence
Once summons are served but before evidence recording begins, amendments require court permission. You must demonstrate valid reasons for the proposed changes.
Common acceptable reasons include discovery of new evidence, change in circumstances, or correction of material errors. The court examines whether the amendment prejudices the respondent’s defense.
During Trial Proceedings
Amendments during trial require stronger justification and court discretion becomes more restrictive. You must show that the amendment is necessary for determining real questions in controversy.
Late amendments may face objections from the opposing party. Courts balance the need for amendment against potential delays and prejudice to proceedings.
Grounds for Allowing Amendments
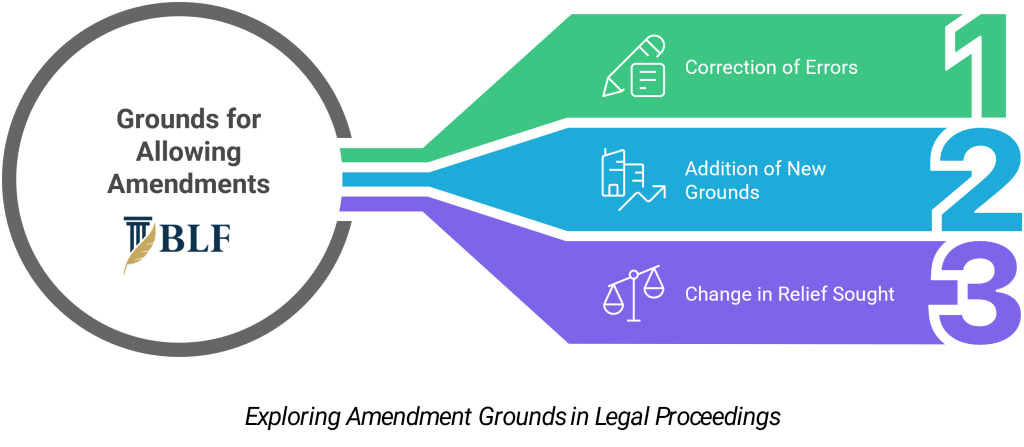
Correction of Errors
Courts readily allow amendments to correct clerical errors, wrong dates, or incorrect personal details. These changes do not affect the substance of the case.
Factual mistakes in names, addresses, or case numbers are typically amended without opposition. Such corrections ensure accurate record-keeping and avoid confusion.
Addition of New Grounds
You can add new grounds for divorce if they arise after filing the original petition. Courts examine whether these grounds are legally valid and supported by evidence.
For instance, if your spouse commits adultery after filing on cruelty grounds, you can amend to include this new ground. The amendment must be based on genuine circumstances.
Change in Relief Sought
Amendments to modify claims for maintenance, custody, or property division are permissible. Courts consider whether the changes reflect genuine developments in circumstances.
You might need to increase maintenance claims due to changed financial situations. Similarly, custody arrangements may require modification based on children’s welfare.
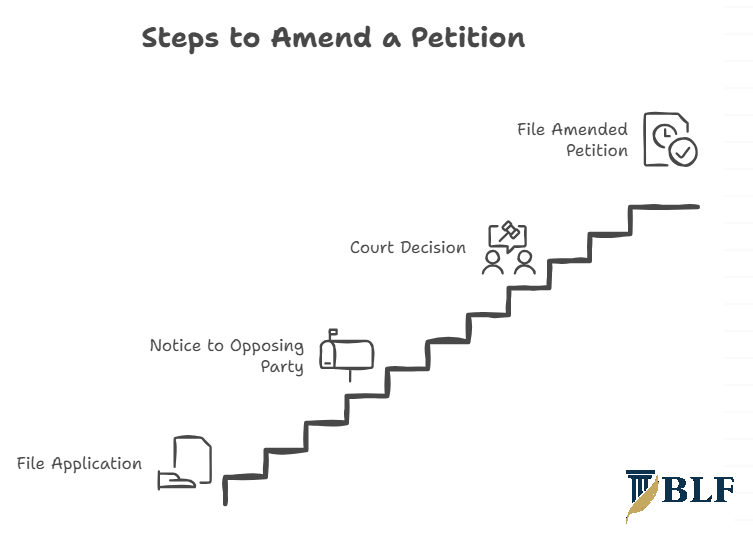
Procedure for Amendment
Filing Application
Submit a formal application under Order 6 Rule 17 CPC to the family court handling your case. The application must specify the proposed amendments with supporting reasons.
Include the amended petition showing changes clearly marked. Pay the prescribed court fees for amendment applications as per court rules.
Notice to Opposing Party
The court issues notice to the respondent regarding your amendment application. They have the opportunity to file objections within the stipulated time frame.
The opposing party can contest the amendment if it prejudices their case or causes undue delay. Courts hear both sides before deciding on the application.
Court Decision
The court examines the necessity and impact of proposed amendments. Factors considered include stage of proceedings, potential prejudice, and interests of justice.
If granted, you must file the amended petition within the specified time. The case then proceeds based on the modified pleadings.
Limitations and Restrictions
Time Constraints
While no absolute time limit exists, delayed amendment applications face greater scrutiny. Courts may refuse amendments that cause unreasonable delays in proceedings.
Applications made close to final hearing dates often face rejection. Early application for amendments improves chances of approval.
Prejudice to Opposing Party
Courts reject amendments that unfairly prejudice the respondent’s defense. The opposing party must have reasonable opportunity to respond to new allegations.
Amendments that completely change the nature of the case may be refused. The principle is to ensure fair proceedings for both parties.
Statutory Limitations
Some amendments may violate statutory provisions or exceed legal limitations. For example, adding grounds not recognized under applicable personal laws would be rejected.
Courts ensure amended petitions comply with relevant marriage laws. The amendment cannot seek relief beyond what the law permits.
Conclusion
Divorce petitions can be amended under Indian law, but success depends on proper timing, valid reasons, and court discretion. Understanding the legal framework and procedural requirements is crucial for effective amendments.
Professional legal guidance ensures your amendment application meets all requirements and maximizes approval chances. Contact Bhatla Law Firm for a free consultation to discuss your specific amendment needs and develop the best strategy for your case.

